Weak_random
from secret import flag
import time
import os
import random
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import os
import hashlib
assert(len(flag)==32)
def padding(message):
padding_len = 16 - len(message)%16
ret = hex(padding_len)[2:].zfill(2)
return bytes.fromhex(ret*padding_len)+message
def get_weak_entropy():
time_now=time.time()%10000
entropy_part1 = int(time_now) & 0xFFFF
entropy_part2 = os.getpid() & 0xFF
final_seed = entropy_part1 + (entropy_part2 << 8)
random.seed(final_seed)
key = random.getrandbits(128)
return key
entropy_key=get_weak_entropy()
iv = os.urandom(16)
key_bytes = entropy_key.to_bytes(16, byteorder='big')
msg=padding(flag.encode())
aes = AES.new(key_bytes,AES.MODE_CBC,iv=iv)
enc = aes.encrypt(msg)
print(enc.hex())
check=hashlib.sha256(flag.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
print(check)
#enc=a4d1a3d4a4c5eee0834449f1ed4539b3b29157825d0dbfa51e84525bb00ed5b5f462e994a2c742baa5fb90977507983c
#check=063043351f9576f5ffeaa565da8edf70dad688fd8b406742fa166de432d1ae27注意到产生随机数的种子是一个小于等于0xFFFF的非负整数和一个小于等于0xFF的非负整数拼接而成的,所以可以考虑爆破,而由padding函数的实现可以发现这里是在消息的前面拼接的,而且flag的长度是32,所以密文的第一块对应的是拼接的数据,那么我们可以将密文的第一块当作IV拿来解密,所以只需要遍历seed尝试用生成的key进行解密即可:
import random
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import hashlib
ct = "a4d1a3d4a4c5eee0834449f1ed4539b3b29157825d0dbfa51e84525bb00ed5b5f462e994a2c742baa5fb90977507983c"
check = "063043351f9576f5ffeaa565da8edf70dad688fd8b406742fa166de432d1ae27"
iv0 = bytes.fromhex(ct[:32])
ct0 = bytes.fromhex(ct[32:])
for entropy_part1 in range(0xFFFF + 1):
for entropy_part2 in range(0xFF + 1):
final_seed = entropy_part1 + (entropy_part2 << 8)
random.seed(final_seed)
key = random.getrandbits(128)
key_bytes = key.to_bytes(16, byteorder='big')
aes = AES.new(key_bytes, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv0)
tmp = aes.decrypt(ct0)
if hashlib.sha256(tmp).hexdigest() == check:
print(tmp.decode('utf-8'))
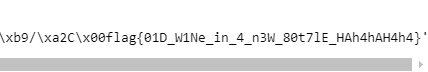
exit(0)可以得到flag:0428f4ff1a4e3d2e2326552f9db48fa9
Simple LLL
首先进行方舟字节码逆向,可以见到Index里面有关于flag的如下代码:
public Object #~@0>#runMixer(Object functionObject, Object newTarget, Index this) {
obj = this.flag;
if ((this.flag.length < 6 ? 1 : 0) != 0) {
this.output = "Flag too short!";
return null;
}
if (istrue(("flag{" != obj.substring(0, 5) ? 1 : 0)) != null || isfalse(("}" != obj[obj.length - 1] ? 1 : 0)) == null) {
this.output = "Invalid flag, must starts with `flag{` and ends with `}`";
return null;
}
substring = obj.substring(5, obj.length - 1);
if ((0 != (substring.length % 3) ? 1 : 0) != 0) {
this.output = "Invalid key length (must be multiple of 3)";
return null;
}
i = 0;
getPrime = this.getPrime(215);
getPrime2 = this.getPrime(128);
getPrime3 = this.getPrime(170);
r36 = [Object];
obj2 = getiterator("Lattice-based cryptography is the generic term for constructions of cryptographic primitives that involve lattices, either in the construction itself or in the security proof.".substring(0, 50));
obj3 = obj2.next;
i2 = 0;
while (true) {
callthisN = obj3();
throw.ifnotobject(callthisN);
if (istrue(callthisN.done) != null) {
break;
}
r362 = callthisN.value;
try {
bytesToLong = this.bytesToLong(substring[i] + substring[i + 1] + substring[i + 2]);
i += 3;
r362 = (i >= substring.length ? 1 : 0);
if (r362 != 0) {
i = 0;
}
r36.push((this.getRandomBits(190) * getPrime) + ((this.modPow(getPrime2, bytesToLong, getPrime3) * BigInt(r362.charCodeAt(0))) % getPrime3));
} catch (ExceptionI0 unused) {
z = r362;
if (istrue(i2) == null) {
i2 = 1;
obj4 = null;
r363 = hole;
try {
obj5 = obj2.return;
obj3 = obj5;
r363 = (0 == obj5 ? 1 : 0);
} catch (ExceptionI0 unused2) {
}
if (r363 == 0) {
obj4 = obj3();
throw(z);
throw.ifnotobject(obj4);
}
}
throw(z);
}
}
this.output = "P: " + getPrime3 + ", G: " + getPrime2 + "\nEncrypted: [" + r36.join(", ") + "]";
console.error("P: " + getPrime3 + "");
console.error("G: " + getPrime2 + "");
i3 = 0;
obj6 = getiterator(r36);
obj7 = obj6.next;
i4 = 0;
while (true) {
callthisN2 = obj7();
throw.ifnotobject(callthisN2);
if (istrue(callthisN2.done) != null) {
return null;
}
r364 = callthisN2.value;
try {
console.error("result[" + i3 + "]: " + r36[i3] + "");
r364 = i3 + 1;
i3 = r364;
} catch (ExceptionI0 unused3) {
z2 = r364;
if (istrue(i4) == null) {
i4 = 1;
obj8 = null;
r365 = hole;
try {
obj9 = obj6.return;
obj7 = obj9;
r365 = (0 == obj9 ? 1 : 0);
} catch (ExceptionI0 unused4) {
}
if (r365 == 0) {
obj8 = obj7();
throw(z2);
throw.ifnotobject(obj8);
}
}
throw(z2);
}
}
}可以知道\(P\)是一个170位的质数,\(G\)是一个128位的质数,还会生成一个215位的质数(记为\(p_0\)),对于flag,首先程序会将flag外面包裹的flag{}去除,然后将剩余部分分为若干个长度为3的字串,设对应数值为\(x_1,x_2,\cdots\),对于\(x_i\)(\(i=1,2,\cdots\)),有:
$$
c_i=q_ip_0+[s_iG^{x_i}\mod{P}]
$$
其中\(s_i\)为Lattice-based cryptography is the generic term for constructions of cryptographic primitives that involve lattices, either in the construction itself or in the security proof.这段话的前50个字符中的第\(i\)个字符对应的ASCII码值,\(q_i\)为一个随机的190位整数,设\(s_iG^{x_i}\mod{P}=r_i\),设一共有\(n\)次这样的运算,则可以得到:
$$
\begin{cases}
c_1=q_1p_0+r_1\\
c_2=q_2p_0+r_2\\
\cdots\\
c_n=q_np_0+r_n\\
\end{cases}
$$
显然这是AGCD问题,\(r_i\)大约为170位,那么可以构造如下格:
$$
\left(\begin{matrix}
2^{171}&c_2&c_3&\cdots&c_{n}\\
&-c_1&&&\\
&&-c_1&&\\
&&&\ddots&\\
&&&&-c_1
\end{matrix}\right)
$$
规约后可以得到一条短向量:
$$
(2^{171}q_1,q_1r_2-q_2r_1,\cdots,q_1r_n-q_nr_0)
$$
提取第一个分量就可以得\(q_1\),从而可以从\(c_1\)中提取出\(r_1\)(有\(c_1\equiv r_1\pmod{q_1}\)),从而恢复出\(p_0\)。
在获取\(p_0\)之后可以知道对于\(i=1,2,\cdots,n\),有\(r_i=c_i\mod{p_0}\)(因为\(r_1<p_0\)),有:
$$
r_i\equiv s_iG^{x_i}\pmod{P}
$$
因为\(s_i\)是已知量,所以可以知道:
$$
G^{x_i}\equiv r_is_i^{-1}\pmod{P}
$$
因为\(x_i\)相对较小,所以通过求解DLP就可以得到所有\(x_i\),从而恢复出flag:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from tqdm import trange
P = 1105340037553808473854838067251286973932436127087387
G = 258698882868391024376029756014412783703
ct = [...]
x0 = ct[0]
x = ct[1:]
L = matrix(ZZ, len(x) + 1, len(x) + 1)
L[0, 0] = 2^171
for i in range(len(x)):
L[0, i+1] = x[i]
L[i+1, i+1] = -x0
res = L.LLL()
q0 = res[0, 0] // 2^171
r0 = ZZ(x0 % q0)
p = ZZ((x0 - r0) // q0)
R = GF(P)
text = "Lattice-based cryptography is the generic term for constructions of cryptographic primitives that involve lattices, either in the construction itself or in the security proof."
flag = b""
for i in trange(len(ct)):
b = ct[i] % p
y = b * inverse(ord(text[i]), P) % P
x = discrete_log(R(y), R(G))
flag += long_to_bytes(x)
print(flag)可以得到:
可以看到这里得到的实际上是flag重复多次的结果,从中可以提取出真正的flag:b5f1a6ca7c28f8ee14b6ca289ed2f061f0f0a01c67e77,包上flag{}就可以了。
Ea5y_RSA
题目描述:
这是一个未完全开发的OpenHarmony应用,在hint.txt中泄露了部分日志记录。请根据给定的源码和日志记录得到flag日志如下:
05-15 18:42:52.831 20328-20328 C03951/InputKeyFlow com.example.ea5y_rsa I [(100000:100000:scope)] Id:1513, click 0 up, state: 0
05-15 18:42:52.831 20328-20328 C0391e/AceGesture com.example.ea5y_rsa I [(100000:100000:scope)] Click try accept
05-15 18:42:52.831 20328-20328 C03951/InputKeyFlow com.example.ea5y_rsa I [(100000:100000:scope)] Click accepted, tag: Button
05-17 18:42:52.848 20328-20328 A03d00/JSAPP com.example.ea5y_rsa I my gift: 0,48,13,6,9,42,134,72,134,247,13,1,1,1,5,0,4,130,2,98,48,130,2,94,2,1,0,2,129,129,0,162,241,252,198,79,226,203,150,170,211,175,5,127,220,154,215,250,190,125,3,43,15,214,239,122,148,175,20,208,173,241,85,168,92,181,110,220,162,25,205,159,96,119,180,19,33,9,52,34,137,4,102,166,195,142,204,1,247,140,141,184,92,14,162,123,208,160,102,112,154,194,130,104,139,141,10,54,148,160,164,100,245,208,41,39,103,160,135,99,108,15,231,219,255,249,35,114,131,108,70,144,182,118,253,222,115,181,71,155,70,135,141,36,73,221,205,146,31,8,55,181,46,111,127,208,101,185,221,2,3,1,0,1,2,129,128,43,13,141,32,72,211,63,191,155,123,58,239,85,13,80,204,104,48,20,143,213,188,229,169,120,213,248,60,163,182,145,225,116,14,170,209,147,242,48,167,39,201,49,87,159,6,71,140,66,227,185,9,246,94,13,72,209,236,58,114,231,151,75,54,47,89,245,211,248,113,162,189,101,189,68,168,165,3,221,23,176,183,78,56,179,150,198,63,126,131,223,165,239,32,59,158,187,205,223,211,228,55,107,19,136,241,169,206,131,34,95,225
05-15 18:42:52.848 20328-20328 C03951/InputKeyFlow com.example.ea5y_rsa I [(100000:100000:scope)] id: 0, log: {types: Click, node: Button, prcd: Down, state: READY, prcd: Up, state: SUCCEED}
05-15 18:42:52.848 20328-20328 C03919/AceInputTracking com.example.ea5y_rsa I [(100000:100000:scope)] Consumed new event id=1513 in ace_container, lastEventInfo: id:-1
05-15 18:42:52.874 20328-20721 C01406/OHOS::RS com.example.ea5y_rsa I RSUIDirector::ProcessMessages messageId:3, cmdCount:1, instanceId:100000
05-15 18:42:52.874 20328-20328 C01406/OHOS::RS com.example.ea5y_rsa I RSUIDirector::PostTask messageId:3, cmdCount:1, instanceId:100000重点在于my gift一段,将其转换为十六进制可以得到:
00300d06092a864886f70d0101010500048202623082025e02010002818100a2f1fcc64fe2cb96aad3af057fdc9ad7fabe7d032b0fd6ef7a94af14d0adf155a85cb56edca219cd9f6077b41321093422890466a6c38ecc01f78c8db85c0ea27bd0a066709ac282688b8d0a3694a0a464f5d0292767a087636c0fe7dbfff92372836c4690b676fdde73b5479b46878d2449ddcd921f0837b52e6f7fd065b9dd02030100010281802b0d8d2048d33fbf9b7b3aef550d50cc6830148fd5bce5a978d5f83ca3b691e1740eaad193f230a727c931579f06478c42e3b909f65e0d48d1ec3a72e7974b362f59f5d3f871a2bd65bd44a8a503dd17b0b74e38b396c63f7e83dfa5ef203b9ebbcddfd3e4376b1388f1a9ce83225fe1仔细查看可以看到有一段3082025e,猜测这是RSA的公钥文件或者私钥文件,提取分块有:
00300d06092a864886f70d010101050004820262
3082025e
020100
0281 # n
81
00a2f1fcc64fe2cb96aad3af057fdc9ad7fabe7d032b0fd6ef7a94af14d0adf155a85cb56edca219cd9f6077b41321093422890466a6c38ecc01f78c8db85c0ea27bd0a066709ac282688b8d0a3694a0a464f5d0292767a087636c0fe7dbfff92372836c4690b676fdde73b5479b46878d2449ddcd921f0837b52e6f7fd065b9dd
0203 # e
010001
0281 # d
80
2b0d8d2048d33fbf9b7b3aef550d50cc6830148fd5bce5a978d5f83ca3b691e1740eaad193f230a727c931579f06478c42e3b909f65e0d48d1ec3a72e7974b362f59f5d3f871a2bd65bd44a8a503dd17b0b74e38b396c63f7e83dfa5ef203b9ebbcddfd3e4376b1388f1a9ce83225fe1可以看到有\(n,e\)还有\(d\)的高位,显然是\(d\)高位泄露,参考2024-高校密码挑战赛赛题一-wp-crypto | 糖醋小鸡块的blog所介绍的方法,大致思路就是设\(d=d_h+d_l\)(其中\(d_h\)为\(d\)已知的高位),构造:
$$
e(d_h+d_l)=k\varphi(n)+1=k(n-p-q+1)+1
$$
因为\(d_h\)已经包含了绝大部分\(d\),那么可以通过:
$$
k= \left\lfloor\frac{e\cdot d_h}{n}\right\rfloor+1
$$
得到\(k\),那么在模\(ed_h\)下可以构造如下多项式:
$$
f(x,y)=1+k(n-y)-ex\pmod{ed_h}
$$
通过多元Coppersmith方法可以求出与\(p+q-1\)大小接近的小根\(x_0\),再通过构造实数方程\(f=x(x_0+x)-n=0\)得到\(p\)的高位,最后再通过Coppersmith恢复\(p\)从而求解出flag。
但是现在缺的是密文,题目给出的工程文件还没用到,可以在Ea5y_rsa\entry\src\main\ets\pages\Index.ets中找到密文:
处理一下就可以通过如下代码求解出flag:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from tqdm import *
import itertools
c = 0x9e5453388afb3fad55c5e34388fb4577ae5508125684a96948c17e83b1626f75581d961cfe480d59e14748cbdc82ca96b8109f32407dd123d00d1ea12af6b1858aea2c083ff3ead15aa65b2fb8570f7b36240f7657cce0c75f2bf7399e912dbc5224d44d4643924021864ad616f771de0aa0c46c23fe5f835fcd92b478b2c8ea
e = 0x10001
n = 0xa2f1fcc64fe2cb96aad3af057fdc9ad7fabe7d032b0fd6ef7a94af14d0adf155a85cb56edca219cd9f6077b41321093422890466a6c38ecc01f78c8db85c0ea27bd0a066709ac282688b8d0a3694a0a464f5d0292767a087636c0fe7dbfff92372836c4690b676fdde73b5479b46878d2449ddcd921f0837b52e6f7fd065b9dd
dhigh = 0x2b0d8d2048d33fbf9b7b3aef550d50cc6830148fd5bce5a978d5f83ca3b691e1740eaad193f230a727c931579f06478c42e3b909f65e0d48d1ec3a72e7974b362f59f5d3f871a2bd65bd44a8a503dd17b0b74e38b396c63f7e83dfa5ef203b9ebbcddfd3e4376b1388f1a9ce83225fe100000000000000000000000000000000
def small_roots(f, bounds, m=1, d=None):
import itertools
if not d:
d = f.degree()
R = f.base_ring()
N = R.cardinality()
k = ZZ(f.coefficients().pop(0))
g = gcd(k, N)
k = R(k/g)
f *= 1/k
f = f.change_ring(ZZ)
G = Sequence([], f.parent())
for i in range(m + 1):
base = N ^ (m - i) * f ^ i
for shifts in itertools.product(range(d), repeat=f.nvariables()):
g = base * prod(map(power, f.variables(), shifts))
G.append(g)
B, monomials = G.coefficients_monomials()
monomials = vector(monomials)
factors = [monomial(*bounds) for monomial in monomials]
for i, factor in enumerate(factors):
B.rescale_col(i, factor)
B = B.dense_matrix().LLL()
B = B.change_ring(QQ)
for i, factor in enumerate(factors):
B.rescale_col(i, 1 / factor)
H = Sequence([], f.parent().change_ring(QQ))
for h in filter(None, B * monomials):
H.append(h)
I = H.ideal()
if I.dimension() == -1:
H.pop()
elif I.dimension() == 0:
roots = []
for root in I.variety(ring=ZZ):
root = tuple(R(root[var]) for var in f.variables())
roots.append(root)
return roots
return []
k = dhigh*e//n+1
hbits = 130
R.<x,y> = Zmod(e*dhigh)[]
f = 1 + k*(n + 1 - y) - e*x
bounds = (2^hbits, 2^500)
res = small_roots(f, bounds, m = 2, d = 2)
print(res)
leak = int(res[0][1])
PR.<x> = PolynomialRing(RealField(1000))
f = x*(leak-x) - n
ph = int(f.roots()[0][0])
PR.<x> = PolynomialRing(Zmod(n))
f = ph + x
res = f.small_roots(X=2^(hbits+6), beta=0.499,epsilon=0.02)[0]
p = int(ph + res)
q = n // p
d = inverse(e,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = pow(c, d, n)
print(long_to_bytes(m))可以得到flag:
实际上通过审计代码可以知道getGift代码如下:
getGift(): number[]{
let gift: number[] = [0];
if(this.keyPair != null){
let pri = this.keyPair.priKey.getEncoded().data;
for(let i: number = 7; i < 285; i++){
gift.push(pri[i]);
}
}
return gift;
}其实就是将私钥文件的前面一部分放到日志里面.
Small Message For (SM4) Encryption
from gmssl import sm4, func
from os import urandom
from flag import FLAG, secret_message
def xor(a, b):
return bytes(x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b))
def encrypt(key, plaintext, iv):
cipher = sm4.CryptSM4(sm4.SM4_ENCRYPT, 0)
cipher.set_key(key, sm4.SM4_ENCRYPT)
ciphertext = cipher.crypt_cbc(iv,plaintext)
return ciphertext
def main():
key = secret_message
while len(key) < 16:
key += secret_message
key = key[:16]
iv = urandom(16)
plaintext = b"My FLAG? If you want it, I'll let you have it... search for it! I left all of it at that place: " + FLAG
assert len(plaintext) % 16 == 0, "The message must be a multiple of 16 bytes."
ciphertext = encrypt(key, plaintext, iv)
print(f"Ciphertext: {ciphertext.hex()}")
print(f"What is this: {xor(key, iv).hex()}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()只给了加密后的flag和\(key\oplus iv\),似乎没有任何切入点,但是看key的生成逻辑可以看到它是secret_message重复多遍得到的,猜测secret_message可能很短,所以考虑爆破,而且给出了一大段明文,可以通过这段明文来判断得到的secret_message是否正确:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmssl import sm4, func
from pwn import xor
from string import digits, ascii_letters
from itertools import product
from tqdm import *
def decrypt(key, ciphertext, iv):
cipher = sm4.CryptSM4(sm4.SM4_ENCRYPT, 0)
cipher.set_key(key, sm4.SM4_DECRYPT)
plaintext = cipher.crypt_cbc(iv, ciphertext)
return plaintext
c = "d9ea43b0d208aa168e4a275a69df3bc86051e756f9ca7959b68c6b23c9e1b69c19e08b75938375a6be830d1844d8a6e368faf1ddffecea69b5abe00ac0d6e10d6696be33d40e83a272072fbe131f98c82587011f61f2d58a020c8c54cf9b651abd740a3d55d36daa9c88cfc10a520ce4211fba4365ce98b82355b17c64dd2de4800fc68df36cfa8a3fd05baac6970dcd"
h = "ee278c4e526ff15b8d308b6b18f83221"
head = b"My FLAG? If you want it, I'll let you have it... search for it! I left all of it at that place: "
key_xor_iv = bytes.fromhex(h)
for l in range(1, 17):
for s in tqdm(product(ascii_letters + digits, repeat=l)):
secret_message = ''.join(s).encode()
key = secret_message
while len(key) < 16:
key += secret_message
key = key[:16]
iv = xor(key_xor_iv, key)
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(c)
pt = decrypt(key, ciphertext, iv)
if head in pt:
print(f"Secret message: {secret_message}")
print(pt)
exit(0)